German functions of words
Sign up for free to get all information about private lessons and our available group courses (A1, A2, B2, B2, C1, C2)
Sign up for freeSign up for free to get all information about private lessons and our available group courses (A1, A2, B2, B2, C1, C2)
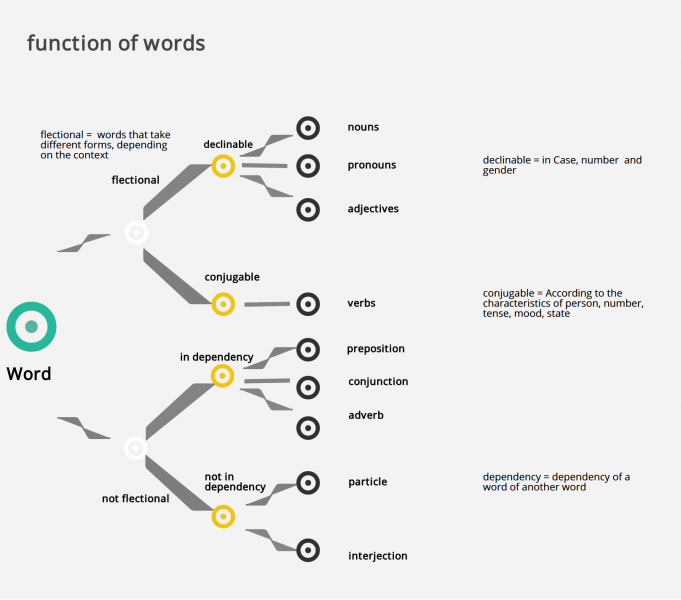
Sign up for freeThe grammatical category of a word is the category to which it belongs. Indeed, all the words can be grouped in the same category according to the characteristics that are similar.
Take online language lessons with a professional teacher
Nouns are categorized in three different categories.
| gender | masculine, feminine, neuter |
|---|---|
| case | nominative, genitive, accusative, dative |
| number | singular, plural |
Die Katzen der Männer sind lieb. - The cats of the men are nice.
| gender | masculine |
|---|---|
| case | genitive |
| number | plural |
Articles accompany a nouns. An article in the narrow sense is the definite and indefinite article of der, die and das. Article can be inflected (declined) and adapt the gender and number of the noun.
Die Katzen der Männer sind lieb. - The cats of the men are nice.
| gender | feminine |
|---|---|
| case | nominative |
| number | plural |
Verbs express actions, events, and states. A verb is the predicate of a sentence. A predicate contains at least one finite verb form (= in number and person defined). Verbs can be inflected (conjugated). A verb expresses Person, number, mood, tense and the active or passive state.
Ich gehe zur Arbeit. - I go to work.
| number | which person (singular or plural ) | 1. person singular |
|---|---|---|
| mood | indicative or subjunctive I / subjunctive II | indicative |
| tense | present, simple past, future I,... | present tense |
| state | active or passive | active |
Adjectives serve to attribute to a living thing, an object, an action, a state, etc., a property, a particular trait. They can have the following functions
| modifier of a noun | das aufregende Spiel | the exciting game |
|---|---|---|
| modifier of an adjective or adverb | typisch türkische Speisen | typical turkish dishes. |
| predicative | das Spiel ist aufregend | the game is exciting |
| adverb | gut Golf spielen | playing golf well |
Adjectives which function as modifier of a noun be inflected in gender, case and number. Adjective are mostly not inflected in other positions of a sentence.
Das Ergebnis der schweren Klausur ist online. - The result of the hard exam is online.
| gender | feminine |
|---|---|
| case | genitive |
| number | singular |
According to the classical definition, a pronoun is a word which stand for another word (a noun). There are seven classes of pronouns.
| personal | a personal pronouns refers to a specific person, a group of people or an object. | Ich sehe dich. | I see you. |
|---|---|---|---|
| possessive | they are used to show, that a noun belongs to somebody or something. | Das ist meine Katze. | That is my cat. |
| demonstrative | these pronouns are used when referring to something that is already defined. | Ja, die sehe ich. | Yes, I see that. |
| interrogative | there are interrogative pronouns, so called "question words". | Wo bist du? | Where are you? |
| reflexive | they are part of the verb which refers to someone. | Ich habe mich geschnitten. | I cut myself. |
| indefinite | they are used to link to subjects or objects that are not defined. | Man kann es schaffen. | It is doable. |
| relative | they describe the nouns more precisely. | Das Mädchen, das Sport mag | The girl, that likes sport. |
The adverb refers to the circumstances in which an action is happening. For example, there are adverbs of time, place and frequency. Adverbs can be used in different situations:
| for a verb | Wir sind dorthin gefahren | We were driving there. |
|---|---|---|
| for an adjective | Das Leben ist besonders schön. | Life is especially nice. |
| for an adverb | Wir sehen uns sehr bald. | We will see us very soon. |
| predicative for nouns | Der Tisch ist dort. | The table is over there. |
| attributive for nouns | Der Tisch dort ist dir. | The table over there is yours. |
Prepositions connect words and groups of words. They refer to a local, temporal, modal or causal relationship between two things.
| temporal | Wir kennen uns seit Ewigkeiten. | We know each other since an eternity. |
|---|---|---|
| modal | Nur mit großem Aufwand gelang es. | Only with great effort was it accomplished |
| causal | Wegen des Unwetters ist alles zerstört. | Because of the storm everything is destroyed |
| local | Die Flasche steht auf dem Tisch. | The bottle is on the table. |
Let's have a look at the following example:
| subject | Maria wirft den Apfel | Maria throws the apple. | subject is always in the nominative case, it is the initial point of an action |
|---|---|---|---|
| predicate | Maria wirft den Apfel. | Maria throws the apple. | central action of a sentence, at least one finite form of verb |
| object | Maria wirft den Apfel. | Maris throws the apple. | accusativeobject (Wen/was?) |
| object | Der Apfel gehört ihr. | The apple is hers. | dativeobject (Wem?) |
| object | Der Apfel ist ihrer. | The apple is hers. | genitiveobject (Wessen?) |
| object | Sie denkt an ihn. | She thinks of him. | prepositional object |